How to avoid scams when completing your tax return
CPA Australia Australians should always be wary of online scams, but we are particularly vulnerable at tax time. Cyber criminals use a mix of tried-and-tested and new methods to attempt…
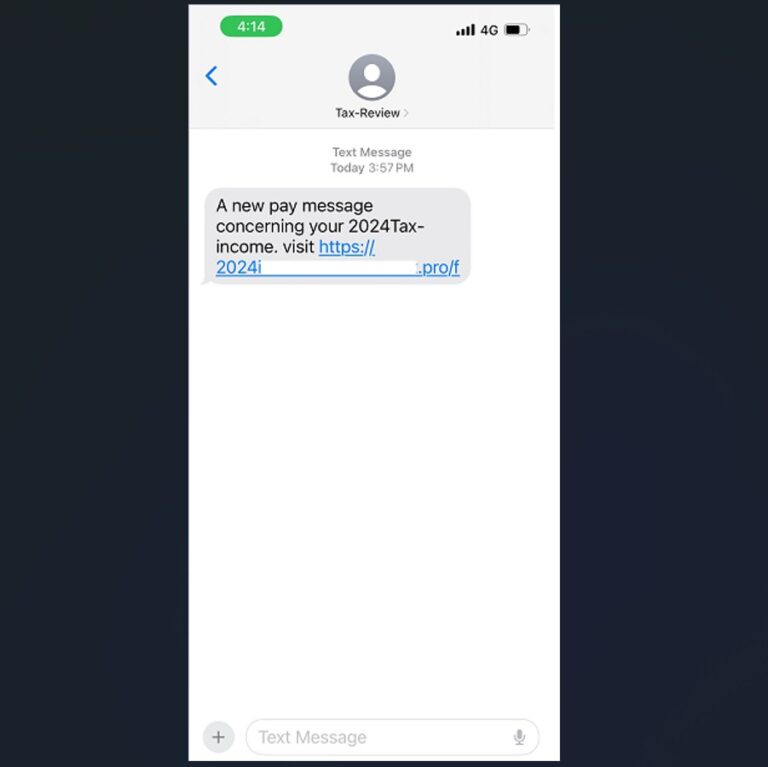
CPA Australia Australians should always be wary of online scams, but we are particularly vulnerable at tax time. Cyber criminals use a mix of tried-and-tested and new methods to attempt…

CPA Australia No one likes being treated as just a number, but with millions of returns and tens of billions of dollars at stake, that’s the reality when it comes…

Looking to give your super a boost before the end of the financial year? Look no further! Follow these five strategies to maximise your contributions and make the most of…

Australian Taxation Office As ‘tax time’ approaches, the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) has announced it will be taking a close look at 3 common errors being made by taxpayers: •…

The first quarter of 2024 saw the Government roll out considerable changes to the Stage 3 Tax Cuts, inflation continuing to slow but remaining stubbornly high across some areas, surging…

When you’re at the helm of your own business, it’s easy to get caught up in the whirlwind of the present – chasing sales, generating leads, and growing your business….

Lady Luck has once again looked down fondly upon Australia, creating the first Federal Budget surplus in 15 years, through a higher tax take on record export earnings and increasing…

By Robert Goudie This savings strategy is about building a healthy deposit and allowing kids to learn about consistent, regular saving. The strategy will require patience to build a substantial…

Depositing cash in a savings account or a term deposit are the most common ways to invest your money. But, how do you know which is right for you? First,…

Here is a list of tips to help you minimise the amount of tax you pay this end of financial year: 1. Keep records Even if you use an accountant…

As the end of financial year fast approaches, there is still time to consider the strategies available to you this June 30 to build your wealth, some of which are…

The Federal Government has delivered a big-spending 2022 budget, taking immediate steps to reduce cost of living pressures for working Australians while implementing a range of massive infrastructure and defence…

If the ins and outs of superannuation leave you confused, the answers to these frequently asked questions will help you understand the basics. How much do I need to retire?…

Did you have a savings account when you were young? It wasn’t uncommon and those old Passbook accounts funded many a first car. Now you’re a parent, are you thinking…

The end of another financial year is looming, and with that may come thoughts about your tax return and how your wealth has tracked throughout the year. Whether you’re nearing…

Some people may think that a financial adviser’s role is to forecast the direction of the share market from month to month and invest clients’ money accordingly. This is not…

With the range of technology and software available today, it’s become easier than ever to work from home. Employees can efficiently complete calls using teleconferencing software, many collaboration tools are…

Thousands of Australians receive tax refunds every year. Some refunds won’t even cover the cost of a pizza to celebrate, however many are quite substantial. If you’re one of the…
End of content
End of content