How to avoid scams when completing your tax return
CPA Australia Australians should always be wary of online scams, but we are particularly vulnerable at tax time. Cyber criminals use a mix of tried-and-tested and new methods to attempt…
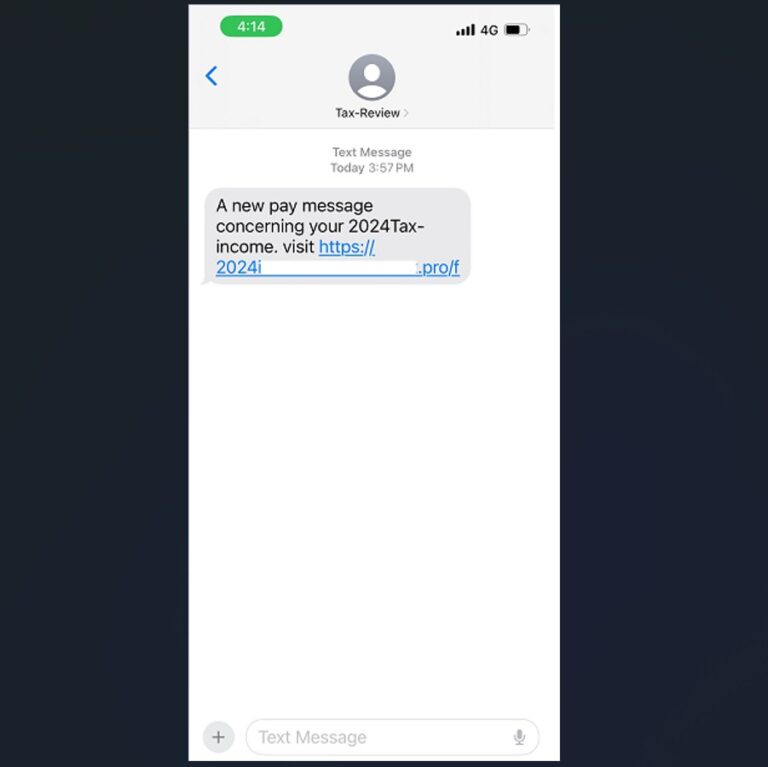
CPA Australia Australians should always be wary of online scams, but we are particularly vulnerable at tax time. Cyber criminals use a mix of tried-and-tested and new methods to attempt…

CPA Australia No one likes being treated as just a number, but with millions of returns and tens of billions of dollars at stake, that’s the reality when it comes…

Looking to give your super a boost before the end of the financial year? Look no further! Follow these five strategies to maximise your contributions and make the most of…

Australian Taxation Office As ‘tax time’ approaches, the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) has announced it will be taking a close look at 3 common errors being made by taxpayers: •…

When you’re at the helm of your own business, it’s easy to get caught up in the whirlwind of the present – chasing sales, generating leads, and growing your business….
Do you have an SMSF with a corporate trustee or are you a director of a company? Do you know you have to register for a director identification number (director…

Here is a list of tips to help you minimise the amount of tax you pay this end of financial year: 1. Keep records Even if you use an accountant…

The Federal Government has delivered a big-spending 2022 budget, taking immediate steps to reduce cost of living pressures for working Australians while implementing a range of massive infrastructure and defence…

The end of another financial year is looming, and with that may come thoughts about your tax return and how your wealth has tracked throughout the year. Whether you’re nearing…

With the range of technology and software available today, it’s become easier than ever to work from home. Employees can efficiently complete calls using teleconferencing software, many collaboration tools are…

Superannuation is for the oldies, right? In some ways that’s true, but even in your twenties there are good reasons to take a bit more interest in your super. The…

Thousands of Australians receive tax refunds every year. Some refunds won’t even cover the cost of a pizza to celebrate, however many are quite substantial. If you’re one of the…
End of content
End of content